5 Signs You Have Gum Disease
 When you think of good oral health, most people imagine bright pearly white teeth, strong pink gums, and fresh breath. A mouth that looks good and smells healthy is the result of excellent oral hygiene and a healthy diet. When a good oral hygiene routine is not maintained, problems begin to arise and can result in serious damage if not treated.
When you think of good oral health, most people imagine bright pearly white teeth, strong pink gums, and fresh breath. A mouth that looks good and smells healthy is the result of excellent oral hygiene and a healthy diet. When a good oral hygiene routine is not maintained, problems begin to arise and can result in serious damage if not treated.
Bacteria: Friend or Foe?
The answer is both. The human mouth has good bacteria that actually protects our teeth and gums. It also has bad bacteria that thrives off sugars and starches that are consumed. This bad bacteria, known as Streptococcus mutans, mixes with mucus and other particles to make up a sticky layer that forms on teeth called plaque. When plaque remains on the teeth, it hardens and forms tartar, which is a hard calcified deposit on the teeth. In most cases, tartar can only be removed by a dentist or dental hygienist.
The 5 Indicators
1. Bleeding Gums
Everyone has experienced bleeding gums at some point in time when brushing their teeth. Bleeding can occur for a number of reasons, including hormonal changes, such as pregnancy, health conditions, and medication. This is the first sign that unhealthy bacteria has begun to move in and stake its claim.
2. Swollen Gums
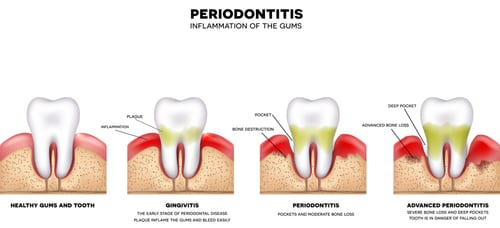
Gums that become red and swollen are a direct result of improper hygiene or none at all. Swollen or inflamed gums is referred to as gingivitis. The bacteria in the plaque sits on the teeth next to the gums and causes irritation, resulting in red, swollen, irritated gum tissue. Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease and can be reversed.
3. Tooth Sensitivity
An excess build up of plaque on the teeth can cause tooth enamel to wear away resulting in sensitivity to the tooth. The enamel protects the tooth, and the tooth becomes more and more sensitive as its protective surface is worn away. Tooth enamel cannot be replenished. Treatment and prevention is the main goal at this stage.
4. Receding Gums
When gingivitis remains untreated, inflammation of the gums around the teeth worsens, and gums begin to pull away from the tooth. This is called periodontitis. Receding gums will eventually expose the root of the tooth if left untreated causing even more problems.
5. Loose or Missing Teeth
When the gums recede, tiny pockets form allowing bacteria to get in and create an infection near or around the root of the tooth. Teeth will begin to loosen because they no longer have the support of the gums and tooth. Ultimately, the tooth will fall out or need to be removed.
How to Restore Oral Health
A professional cleaning by your dentist is the only way to remove tartar from your teeth. Regular office visits with your dentist should be done twice a year. During a dental appointment, your dentist will do a risk assessment and evaluation in order to create a treatment plan that fits your specific needs.
Gingivitis, which includes, bleeding gums, inflamed or swollen gums, and tooth sensitivity, can be reversed with daily brushing, flossing, and regular cleanings by a dentist. However, periodontitis may require further treatment. In this case, a dentist may recommend a deep cleaning, also called Scaling and Root Planing, to scrape off tartar and eliminate rough spots on tooth roots. In more extreme cases, removal of teeth, surgery, bone grafts, and gum grafts may be required.
For more information about Scaling and Root Planing or a consultation with Dr. Salamati, call (310) 275-1090.
